Communication starts with an introduction. Introducing oneself is essential in various interactions. Learn how to introduce yourself in Sanskrit with examples and basic pronouns.
Basic Self Introduction Sentences
| Sanskrit | English Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| भवत: नाम किम् ? | What is your name? (For Male) | For addressing male |
| मम नाम मोहन: | My name is Mohan. | |
| भवत्या: नाम किम् ? | What is your name? (For Female) | For addressing female |
| मम नाम सीता: | My name is Sita. |
Introduction to Pronouns in Sanskrit
| Pronoun | Meaning |
|---|---|
| स: | He (Far Male) |
| सा | She (Far Female) |
| तत् | It (Far Object) |
| क: | Who (Male) |
| का | Who (Female) |
| किम् | Who (Third Object) |
Pronouns Usage Examples
- स: क:? – Who is he?
- स: नायक: – He is an actor.
- सा का? – Who is she?
- सा बालिका – She is a child.
- तत् किम्? – What is that?
- तत् पुष्पम् – That is a flower.
Near Pronouns (एष: / एषा: / एतत्:)
- एष: – He (Near Male)
- एषा: – She (Near Female)
- एतत्: – It (Near Object)
Second Person Pronouns (Two and All)
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| तौ | Those two (Males) |
| ते | Those two (Females or Objects) |
| ते बालका: गच्छन्ति | All boys are going. |
| ता महिला: गच्छन्ति | All girls are going. |
| तानि फलानि पतन्ति | All fruits are falling. |
Examples of Dual and Plural Pronouns
- मूषकौ खादतः – Two mice are eating.
- बालौ हसतः – Two boys are laughing.
- अजे चरतः – Two goats are eating.
- महिले गायतः – Two girls are singing.
Myself and Addressing Others
- अहम् – Myself
- भवान् – You (Male)
- भवती – You (Female)
- आवां – We Two
- वयं – We All
Possessive Pronouns Examples
- रामस्य – Ram’s
- फलस्य – Fruit’s
- घटया: – Watch’s
- दशरथस्य पुत्र: राम: – Dasharatha’s son is Ram.
- सीताया: पति: राम: – Sita’s husband is Ram.
Chapter 2: Sanskrit Components (अव्यय)
Learn important Sanskrit words related to location and time that enhance communication.
Location-Based Components
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| अस्ति | Available |
| नास्ति | Not available |
| अत्र | Here |
| अन्यत्र | Anywhere else |
| तत्र | There |
| कुत्र | Where? |
| सर्वत्र | Everywhere |
Examples:
- राम: अत्र पठति – Ram is reading here.
- सुरेश: तत्र लिखति – Suresh is writing there.
- मोहन: कुत्र गच्छति – Where is Mohan going?
- सीता अन्यत्र अस्ति – Sita is somewhere else.
Time-Related Components
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| अद्य | Today |
| श्व: | Tomorrow |
| परश्व: | Day after tomorrow |
| ह्या: | Yesterday |
| परह्या: | Day before yesterday |
Examples:
- अद्य मंगलवासर: अस्ति – Today is Tuesday.
- ह्या मंगलवासर: अस्ति – Yesterday was Tuesday.
Directional Words
- पुरत: – In front
- पृष्ठत: – Behind
- वामत: – Left
- दक्षिणत: – Right
- उपरि – Over
- अध: – Under
Learn Sanskrit: Self Introduction, Pronouns, Components, and Vibhakti
How to Introduce Yourself in Sanskrit
Communication starts from introduction. Introducing oneself is important to build connections and do any deals. Let’s learn how to introduce yourself in Sanskrit.
| Sanskrit | English Meaning |
|---|---|
| भवत: नाम किम् ? (Male) | What is your name? |
| मम नाम मोहन:। | My name is Mohan. |
| भवत्या: नाम किम् ? (Female) | What is your name? |
| मम नाम सीता:। | My name is Sita. |
Introduction to Pronouns
| Sanskrit | Meaning |
|---|---|
| स: | He |
| सा | She |
| तत् | It |
| क: | Who (Male) |
| का | Who (Female) |
| किम् | Who (Object/Thing) |
Example Sentences
- स: क:? – Who is he?
- स: नायक:। – He is an actor.
- सा का? – Who is she?
- सा बालिका। – She is a girl.
- तत् किम्? – What is that?
- तत् पुष्पम्। – That is a flower.
Second Verse Pronouns (Dual Form)
- तौ – Those two (Males)
- ते – Those two (Females or Neuters)
Examples:
- मूषकौ खादत: – Two mice are eating.
- बालौ हसत: – Two children are laughing.
- अहे चरत: – Two goats are grazing.
- महिले गदत: – Two girls are singing.
Multi Verse Pronouns (Plural Form)
- ते – All (Males)
- ता: – All (Females)
- तानि – All (Objects)
Examples:
- ते बालका: गच्छन्ति – All boys are going.
- ता महिला: गच्छन्ति – All girls are going.
- तानि फलानि पतन्ति – All fruits are falling.
Important Components (अव्यय)
1. Location Related
- अस्ति – Available
- नास्ति – Not available
- अत्र – Here
- तत्र – There
- अन्यत्र – Somewhere else
- कुत्र – Where?
- सर्वत्र – Everywhere
2. Tense Related
- अद्य – Today
- ह्या – Yesterday
- श्व: – Tomorrow
- परश्व: – Day after tomorrow
3. Related Components (बुरुद्धार्थक अव्यय)
| Sanskrit | Meaning |
|---|---|
| शिघ्रम् | Fast |
| मन्दम् | Slowly |
| उच्चै: | Loudly |
| शनै: | Softly |
| कथम् | How |
| सम्यक् | Properly |
| किमर्थम् | Why |
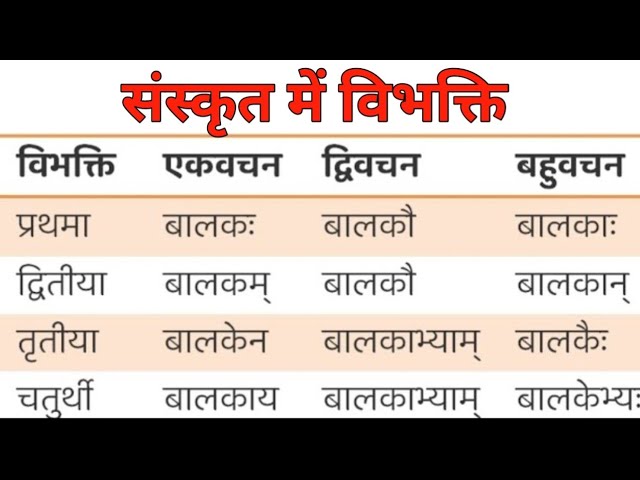
Chapter 3: Sanskrit Inflection (विभक्ति)
1. First Inflection (प्रथमा विभक्ति)
- राधा पाठशालां गच्छति। – Radha goes to school.
- सुमन गीतं गायति। – Suman sings a song.
2. Second Inflection (द्वितीया विभक्ति)
Karma Karaka (Object’s case)
- राम: ग्रन्थम् पठति। – Ram reads the book.
- बालक: नदीं पश्यति। – The child watches the river.
- अहं शाकम् खादामि। – I eat vegetables.
- वयम् अभ्यासम् कुर्म:। – We do exercises.